Lowland Tapir


The lowland tapir is the largest land mammal in Brazil, and the second-largest in South America. They can weigh up to 300 kg and are almost 2.5m long.
from 150kg to 300kg
up to 2.42m long
22 years in the wild
Important data
MAIN FEATURES
Lowland tapirs have a mane that goes from their necks to heads. Adults are dark brown, while youngsters are brown with white horizontal stripes. The tips of their ears are white.
TOP THREATS
Predatory hunting and the destruction of its natural habitat. Its predators are big cats, such as jaguars.
DIET
Fruit, leaves, sprouts, tree bark, small branches, and aquatic plants.REPRODUCTION
There is no defined period for reproduction, but the females go into heat every 80 days. Each pregnancy lasts up to 15 months and only one calf is born.BEHAVIOR
● They are solitary animals.
● They can swim very well, including wide rivers, such as the Amazon.
● When they walk slowly, their heads are lowered.
● When they run, they keep their heads up.
HABITS
Predominantly active at night and in the twilight, with a living area of up to 24 km.
TRIVIA
Due to the large amount of fruit they eat, lowland tapirs help spread seeds through feces, so they are especially important animals in the regeneration and maintenance of forests.
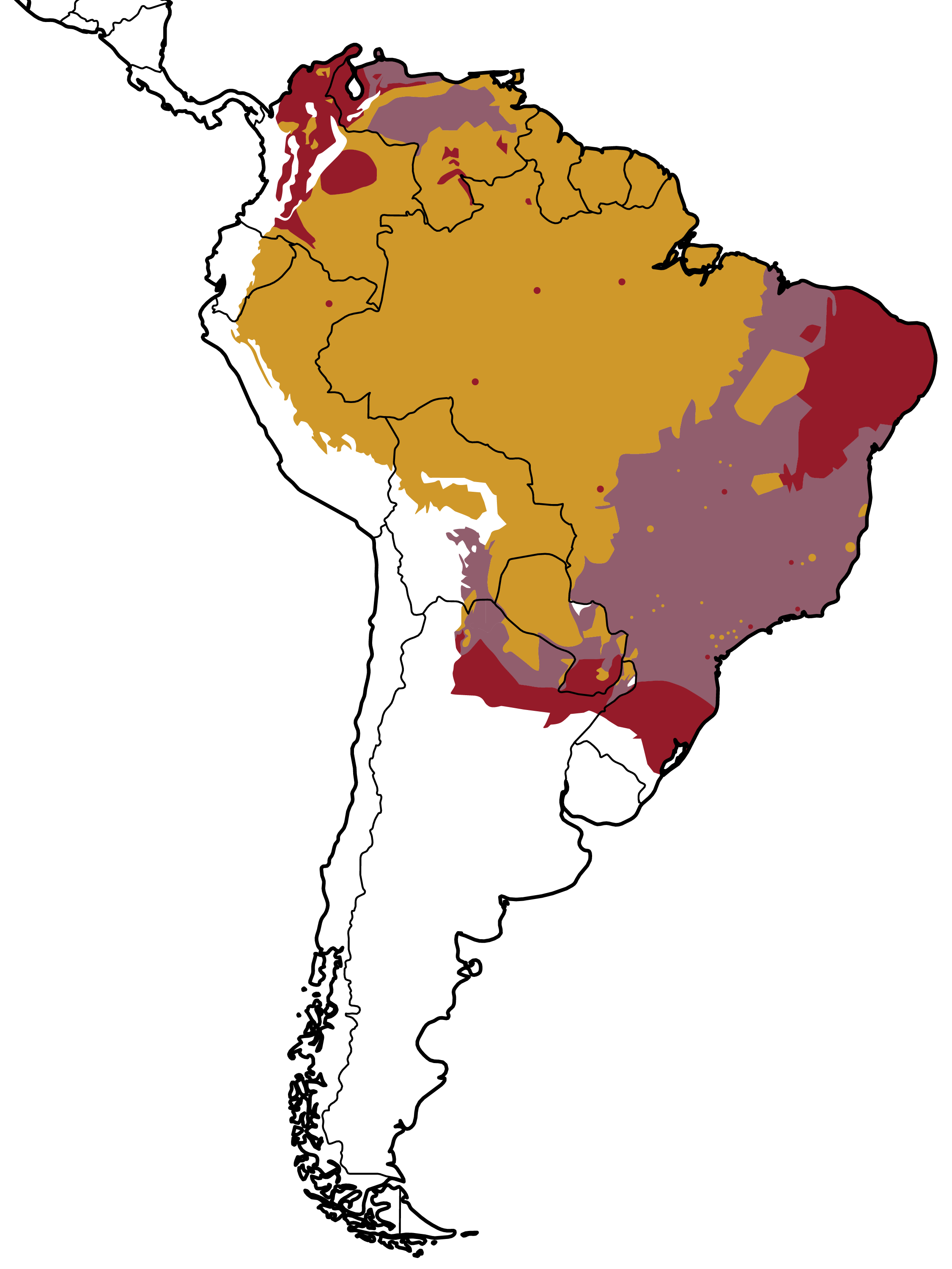
Geographical distribution